| ANTIMONY ACETATE |
|
PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION
|
| CAS
NO. |
3643-76-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
|
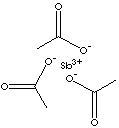
| FORMULA |
Sb(CH3COO)3 |
| MOL
WT. |
298.89 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2915.29 |
| SMILES |
|
| TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3730 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Antimony [III] Acetate; |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
127 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.23 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
| pH |
|
| NFPA
RATING |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
Antimony is a semi-metallic chemical element in Group Va of the periodic table;
atomic number 51; atomic mass 121.75; melting point ca 630.7 C; boiling point
at 1,750 C; specific gravity 6.69 at 20 C; valence 0, +3, -3, or +5.;
electronic config. [Kr]4d10 5s2 5p3. There are four allotropic forms. The common
and stable form is a very brittle, blue-white, hexagonal mineral and has a
rhombohedral crystalline structure. Yellow and black antimony shows the
properties of unstable non-metals. It is a poor conductor of heat and
electricity and is easily powdered to be used by itself. The chief ore of
antimony is stibnite (Sb2S3,
antimony trisulfide) which is produced in China and
covers three-fourths of the world's mined antimony. It is also found in
isomorphous mixture with arsenic, as allemonite. Substantial quantity of
antimony are produced as a by-product in the smelting of base metal ores also.
The pure antimony is produced from the ore by roasting it to form the oxide,
then reducing the oxide with carbon or iron. Antimony is soluble in hot nitric
or sulfuric acid and reacts with oxidizing acids and halogens (fluorine,
chlorine, or bromine). It does not react with water at room temperature but will
ignite and burn in air at higher temperatures. To make stronger, brittle,
solidification expanded and low melting point metals, antimony is mixed with
other metals such as lead and zinc alloys which are used in solder, bearings,
castings, safety matches, and as a red pigment in paint as well as as a hardner
in lead storage batteries, the most important use of antimony metal. Antimony is
being the important element in the semiconductor industry to make diodes,
infrared detectors, and Hall-effect devices. Antimony tartrate was used as an
emetic and expectorant, to produce sweating, and treat people infected with
parasites, but is poisonous and has toxic side effects. Mined antimony is
combined with oxygen to form antimony oxide, one of the most important antimony
compounds. Antimony oxide is a white rhombic crystals; melting at 656°C;
insoluble in water; powerful reducing agent. Most antimony oxide produced is
added to textiles and plastics as fire retardant. It is also used in paints,
ceramics and fireworks, and as enamels for plastics, metal and glass. Antimony
oxides don't react as flame retardants directly. They are used as synergists to
enhance the activity of halogenated flame retardants by stepwise releasing the
halogenated radicals to retard gas phase chain reaction of flame spread. There
are many antimony compounds for industrial uses;
- Antimony
Acetate [Sb(CH3COO)3,
CAS RN: 3643-76-3] Catalyst in the
productionn of synthetic fibers.
- Antimony Pentachloride
[SbCl5,
CAS RN: 7647-18-9] yellow to red oily hygroscopic
liquid; soluble in hydrochloric acid and chloroform; solidifies with
moisture and decomposes in excess
water; used as an intermediate in synthesis and dyeing, used in analytical testing
for cesium and alkaloids.
- Antimony
Pentafluoride [SbF5,
CAS RN: 7783-70-2] moderately viscous liquid;
corrosive
and hygroscopic; reacts violently with water; soluble
in glacial acetic acid; used as a fluorination agent
in organic
synthesis.
- Antimony Pentasulfide [Sb2S5,
CAS RN: 1315-04-4] Also known antimony red, an yellow
to orange powder;
insoluble in water; soluble in alkal and in concentrated hydrochloric acid;
used as a red pigment.
- Antimony Potassium Tartrate [K2[Sb2(C4H4O6)2]·3H2O,
CAS
RN; 11071-15-1] white crystalline powder with a sweetish taste
It is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying
as well as an analytical reagent and flux additive
for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides
or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or
as an emetic and expectorant.
- Antimony Sulfate [Sb2(SO4)3,
CAS RN: 7446-32-4]
white deliquescent powder; soluble in
acids; used in organic synthesis.
- Antimony Trichloride [SbCl3,
CAS RN: 10025-91-9] Orthorhombic deliquescent hygroscopic
crystals;
soluble in
alcohol and acetone; reacts with moisture forming antimony oxychloride in air; used as a chlorinating agent, as
a fireproofing agent in textiles; in bronzing steel
and as a mordant in dyeing as well as a caustic in medicine.
- Antimony Trifluoride
[SbF3,
CAS RN: 7783-56-4] orthorombic deliquescent crystals;
soluble in water; used as
a fluorination agent in organic
synthesis, in dying and to make porcelain and pottery.
- Antimony Triiodide [SbI3,
CAS RN:7790-44-5]
- Antimony Trioxide [Sb2O3,
CAS RN; 1327-33-9 (base), 1309-64-4 (trioxide),
1332-81-6 (tetraoxide), 1314-60-9 (pentaoxide)] white rhombic crystals;
insoluble in water; melts at 656 C;
used as a powerful reducing agent, flame
retardant for wide range of plastics, rubbers, paper and textiles, catalyst in
pet production, activator in glass industry, flocculant in titanium dioxide
production, paints and adhesives industries, ceramic
frites.
- Antimony Trisulfide [Sb2S3,
CAS RN; 1345-04-6]
Dark orange to black rhombic crystals; insoluble in water; melts at 546 C; soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid
and sulfides, used as a
pigment, and in pyrotechnics; used on safety matches and in
vulcanizing rubber; used in combination with antimony oxides as a yellow pigment in glass and
porcelain;
- Potassium Antimonate
[KSbO3,
CAS RN; ]
white powder; soluble in water; used
as an oxidizing agent at high temperature; fire proofing auxiliary; enamel opacifier;
as a glass fining agent and a decolorizer
in glass tubes and fiber glass.
- Sodium Antimonate [NaSbO3,
CAS RN; 15432-85-6]
white powder; soluble in water; used
as an oxidizing agent at high temperature; fire proofing auxiliary; enamel opacifier;
as a glass fining agent and a decolorizer
in glass tubes and fiber glass.
- Minor
compounds
- Antimony monosulfide
[CAS RN; 12067-17-3]
- Antimony tetramer [CAS
RN; 12597-17-0]
- Antimony(III) isopropoxide [CAS
RN; 18770-47-3]
- Antimony(III) methoxide
- Antimony(III)ethoxide [CAS
RN; 10433-06-4]
- Chlorofluorotrimethylantimony [CAS
RN; 13077-54-8]
- Chlorohydroxytriphenylantimony
[CAS RN; 36368-97-5
- Ddichlorotris(4-bromophenyl)antimony [CAS
RN;
125716-16-7
- Diantimony diselenide [CAS
RN; 12294-12-1]
- Diantimony tetrasulfide
[CAS RN; 12359-48-7]
- Diantimony triselenide [CAS
RN; 1315-05-5]
- Dibromotributylantimony [CAS
RN; 16629-56-4
- Dichlorotribenzylantimony
[CAS RN; 19493-17-5
- Dioxygenyl hexafluoroantimonate [CAS
RN; 12361-66-9]
- Diphenyl(o-tolyl)antimony [CAS
RN; 312308-62-6
- Hexafluoroantimonic acid [CAS
RN; 16950-06-4]
- Lithium hexafluoroantimonate(V)
[CAS RN; 18424-17-4]
- Magic acid
(fluorosulfuric acid-antimony pentafluoride ) [CAS RN; 23854-38-8]
- Nitronium
hexafluoroantimonate(V) [CAS RN; 17856-92-7]
- Nitrosonium (nitrosyl) hexafluoroantimonate
[CAS RN; 16941-06-3]
- Potassium
hexahydroxoantimonate(V) 12208-13-8
- Potassium antimonyl
tartrate trihydrate [CAS RN; 28300-74-5]
- Potassium hexafluoroantimonate
- Potassium hexafluoroantimonate(V) 16893-92-8
- Potassium Pyroantimonate
[CAS RN; 10090-54-7]
- Potassium Pyroantimonate, [CAS
RN; 29638-69-5]
- Silver (I) hexafluoroantimonate [CAS
RN; 26042-64-8]
- Sodium
hexafluoroantimonate [CAS RN; 16925-25-0]
- Sodium
thioantimonate(V) 10101-91-4
- Tetrabutylantimony(v)
bromide, [CAS RN; 45212-19-9]
- Tetraphenylantimony bromide [CAS
RN; 16894-69-2]
- Triantimony disulfide [CAS
RN; 107373-21-7]
- Triethyloxonium hexachloroantimonate
3264-67-3
- Trimethylantimony bromide[CAS
RN; 5835-64-3]
- Trimethylantimony dichloride
[CAS RN; 13059-67-1]
- Trimethylantimony diiodide [CAS
RN; 13077-53-7]
- trimethyloxonium
hexachlorantimonate [CAS RN; 54075-76-2]
- Triphenylantimony
[CAS RN; 603-36-1]
- Triphenylantimony diacetate [CAS
RN; 1538-62-1]
- Triphenylantimony dibenzoate [CAS
RN; 57997-56-5]
- Triphenylantimony dichloride [CAS
RN; 594-31-0]
- Triphenylantimony sulfide [CAS
RN; 3958-19-8]
- Triphenylcarbenium hexachloroantimonate [CAS
RN; 52704-88-8]
- Triphenylthioantimonate
[CAS RN; 28609-58-7]
- Tris(1-naphthyl)antimony [CAS
RN; 27309-70-2]
- Tris(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)antimony [CAS
RN; 386-91-4]
- Tris(4-bromophenyl)aminium hexachloroantimonate [CAS
RN; 24964-91-8]
- Tris(4-bromophenyl)antimony [CAS
RN; 17946-45-1]
- Tris(dimethylamino)antimony [CAS
RN; 7289-92-1]
- Tris(o-tolyl)antimony [CAS
RN; 23822-15-3]
- Tris(p-tolyl)antimony [CAS
RN;
5395-43-7]
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
powder |
| An |
22.0%
min |
| CHLORIDES |
0.01%
max |
| IRON |
0.002%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
plastic drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: 20/22-36/37/38,
Safety Phrases: 22-26-36 |
|
